Lifeguards for Different Aquatic Conditions
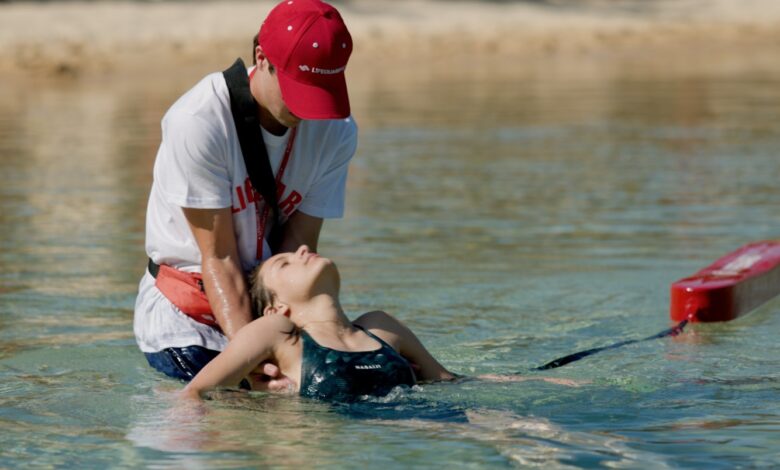

Lifeguards are essential figures in ensuring the safety of people in aquatic environments. From pools to beaches, water parks to rivers, each setting presents unique challenges that require specific training and mastery.
In this article, we’ll dig into the different sorts of lifeguards for different aquatic conditions, their training requirements, and the significance of certifications like those presented by the American Lifeguard Association (ALA).
Pool Lifeguards
Pool lifeguards are stationed in controlled environments like public and confidential swimming pools. Their essential obligation is to screen swimmers, uphold safety runs, and respond swiftly to emergencies. Lifeguards go through rigorous training in lifeguard classes to master essential skills, for example, water rescue techniques, CPR, AED use, and first aid specific to pool settings.
Lifeguard trainingcentres around reconnaissance, perceiving distressed swimmers, successful communication with patrons, and organizing with different lifeguards and staff during emergencies. Pool lifeguards should likewise remain updated on facility-specific protocols and safety procedures to ensure a protected swimming environment for all.
Beach Lifeguards
Beach lifeguards work in unique and testing environments, including ocean beaches and seaside regions. They face a scope of hazards, for example, rip currents, evolving tides, waves, marine life experiences, and capricious weather patterns. Lifeguards watching beaches go through broad training to deal with untamed water rescues, spinal wounds from wave effects, and first aid for marine life stings and nibbles.
Beach lifeguards likewise instruct beachgoers about water safety, including the dangers of rip currents, how to identify safe swimming regions, and the significance of remaining inside assigned zones. Their training incorporates utilizing rescue equipment like rescue sheets, tubes, and individual watercraft to quickly reach and help distressed swimmers.
Water Park Lifeguards
Water park lifeguards work in event congregation settings with different water attractions, for example, slides, wave pools, lethargic rivers, and sprinkle cushions. They are prepared to ensure visitor safety by observing water activities, upholding level and safety requirements on rides, and responding to emergencies quickly.
Lifeguards at water parks go through specialized training in slide rescue techniques, swarm management, visitor interaction, and emergency response protocols specific to water park environments. They should likewise be capable of CPR, first aid, and AED use, as well as working rescue equipment like rescue tubes and backboards.
Waterway and Lake Lifeguards
Lifeguards watching rivers, lakes, and other normal waterways face unique challenges contrasted with pool and beach environments. They manage solid currents, underwater hazards, restricted permeability, and potential dangers like lowered articles and aquatic wildlife.
Stream and lake lifeguards get specialized training in swift water rescue techniques, involving watercraft for rescues, surveying water conditions, and discussing successfully with different responders. They should likewise know about local water guidelines, hazards specific to the area, and emergency clearing procedures.
Aquatic Facility Lifeguards
Aquatic facility lifeguards work in various settings, including community pools, fitness focuses, water treatment facilities, and exclusive hangouts. They are answerable for ensuring the safety and well-being of patrons by checking pool activities, authorizing rules, giving first aid when required, and responding to emergencies expeditiously.
Lifeguards at aquatic facilities go through far-reaching training that covers water rescue skills, CPR, AED use, first aid techniques, facility-specific protocols, and visitor interaction. They should likewise be knowledgeable about water science, pool maintenance, and emergency departure procedures.
Training for Lifeguards
Lifeguard training programs are intended to prepare people for the challenges they might experience in different aquatic environments. These programs normally incorporate study hall guidance, involved training, situation-based reproductions, and certification tests to survey competency.
During lifeguard training, members master essential skills, for example, reconnaissance techniques, perceiving indications of distress in swimmers, performing water rescues utilizing different techniques and equipment, controlling CPR and first aid, and organizing with different lifeguards and emergency responders.
Certification and Recertification
Lifeguards should get and keep up with substantial certifications to work in aquatic environments. Certification programs, like those presented by the American Lifeguard Association (ALA), ensure that lifeguards fulfil industry guidelines and are fit for responding actually to emergencies.
Certification courses cover a scope of themes, including water rescue skills, CPR, AED use, first aid, emergency action plans, legal contemplations, and risk management. Lifeguards should likewise go through regular recertification to remain updated on new protocols, refresh their skills, and show continuous competency.
Adjusting to Changing Environments
Lifeguards should be versatile and ready to change their systems and techniques in light of the specific aquatic conditions they experience. This incorporates understanding water profundities, currents, permeability, atmospheric conditions, expected hazards, and visitor conduct.
Powerful lifeguarding includes nonstop assessment of environmental elements, proactive observation, quick decision-production during emergencies, clear communication with patrons and partners, and cooperation with other emergency responders when required.
Persistent Professional Development
To upgrade their capabilities and remain current with best practices, lifeguards participate in constant professional development. This incorporates going to studios, workshops, and meetings connected with water safety, lifeguarding techniques, emergency response, and risk management.
Professional development opportunities additionally incorporate taking part in reproduced rescue situations, drills, and exercises to rehearse skills, further develop teamwork, and upgrade readiness for genuine emergencies. Lifeguards may likewise pursue advanced certifications in regions, for example, water rescue, lifeguard management, and aquatic facility operations.
Community Engagement and Education
Lifeguards play an essential role in educating the public about water safety, drowning prevention, and the significance of observing guidelines and rules in aquatic settings. They collaborate with community members, school gatherings, and recreational programs to advance a culture of safety and mindfulness.
Community outreach endeavours might incorporate directing water safety introductions, driving swim examples and studios, coordinating CPR and first aid training sessions, disseminating educational materials, and partaking in public events zeroed in on water safety and drowning prevention.
Final Word
Different lifeguards are prepared to deal with specific aquatic conditions, from pool environments to vast water settings, water parks, rivers, lakes, and aquatic facilities. Lifeguard training programs furnish people with essential skills for water rescue, first aid, CPR, AED use, and emergency response, setting them up to respond really to different situations.
Certifications like those presented by the American Lifeguard Association (ALA) ensure that lifeguards satisfy industry guidelines and are fit to give a protected environment to swimmers and visitors. Lifeguards should continually adjust their systems, remain updated on new protocols, and participate in constant professional development to improve their capabilities and advance water safety in their communities.